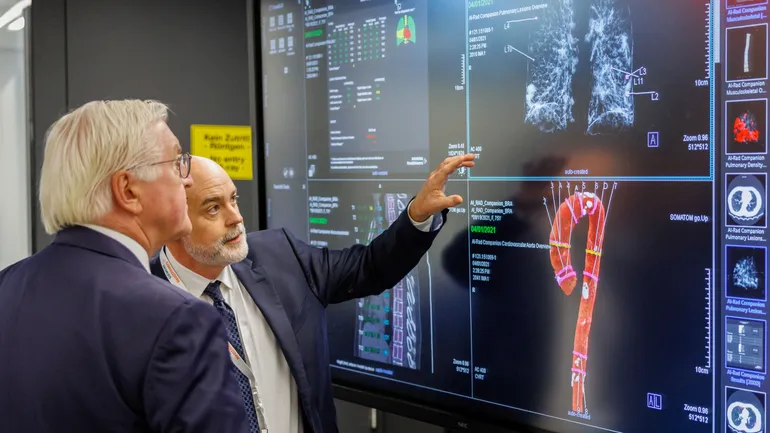
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into medical devices has seen a dramatic increase over the past decade, facilitated by advancements in connectivity and technology as well as significant investments in AI capabilities. According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) database, 950 AI or ML-enabled devices were authorized up to August 7, 2024, marking a substantial rise from just six approvals in 2015 to 221 authorizations in 2023 alone.
Numerous large medtech companies, such as GE Healthcare, Siemens Healthineers, and Medtronic, have been incorporating AI into their equipment. In addition, tech giants like Apple and chipmaker Nvidia are entering the healthcare sector, contributing to the development of AI applications in medical diagnostics and treatment. Apple, for example, has developed AI features for its watches to monitor heart arrhythmias, while Nvidia has collaborated with companies like Medtronic and Johnson & Johnson.
AI applications are largely concentrated in the field of radiology, where they enhance imaging quality, reduce scan times, assist in patient positioning, optimize radiation doses, and flag potential medical conditions. Over three-quarters of AI applications authorized by the FDA support these radiological functions. Cardiovascular medicine, where AI aids in detecting arrhythmias and signs of heart failure, is the second most popular specialty for these devices. Other developing areas include robotic surgery, where AI can offer critical data integration and visual aids during procedures.
These AI-enabled devices typically gain FDA clearance through the 510(k) pathway, a less rigorous and more cost-effective process requiring that new devices be substantially equivalent to existing products. This has been the pathway for about 97% of AI device approvals as of August 2024. Other devices go through de novo classification for moderate-risk innovations or premarket approval for higher-risk scenarios.
Technological advancements and AI integration hold potential for significant improvements in patient diagnostics and treatment processes by making medical procedures more efficient and accurate. However, despite the promising advancements, experts insist that AI enhancements are designed to support, rather than replace, the critical decisions made by healthcare professionals. The future of AI in healthcare seems geared towards multimodal AI, which integrates varied data such as imaging, lab results, and patient histories to better assist clinical decision-making.
While the technological and medical sectors continue to explore and expand the capabilities of AI in healthcare, the FDA and medical professionals remain cautious, ensuring these tools meet stringent safety and effectiveness standards set to protect patient health.
#number #medical #devices #spiked #decade